Self-Assembling Peptides as a Bioink
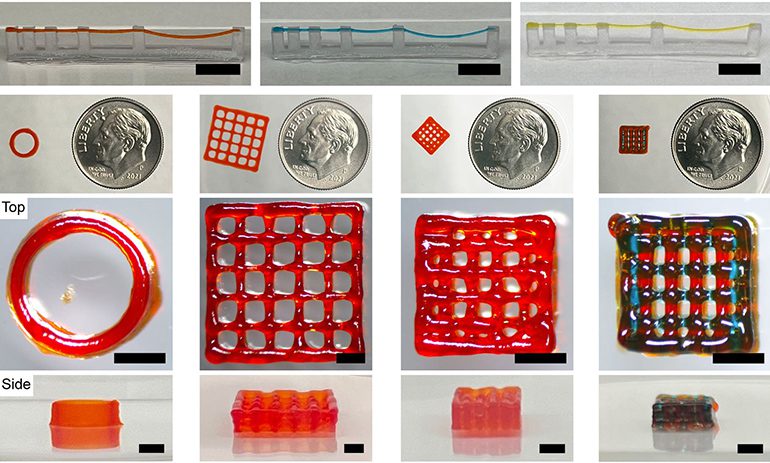
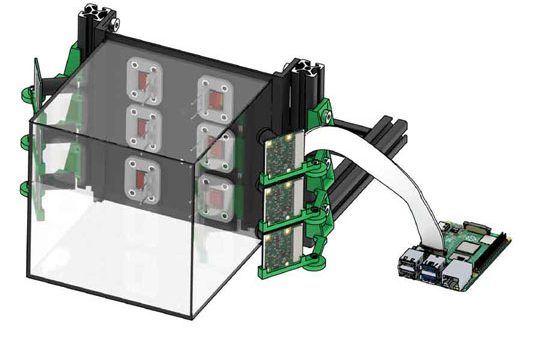
Researchers at Rice University have developed a bioprinting method that uses self-assembling peptides as a bioink. The technique involves using “multidomain peptides” that are hydrophobic at one end and hydrophilic at the other. When the peptides encounter water, they flip over each other to create hydrophobic sandwich structures that stack together to form fibers, creating the base structure of the printed hydrogel. This self-assembly helps the printed material to rapidly form a structure, and it will also reform after deformation. What makes the peptides highly suited for use in implanted constructs is their track record of safe use in the […]…
Continue Reading