 WHONET 5 is a database software for the management of microbiology laboratory test results.
WHONET 5 is a database software for the management of microbiology laboratory test results.
The principal goals of the software are:
- to enhance local use of laboratory data; and
- to promote collaboration through the exchange of data between centres.
The software was developed for the management of routine laboratory results but has also been used for research studies. Software development has focused on data analysis, particularly of the results of antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
WHONET analytical tools can facilitate:
- the selection of antimicrobial agents;
- the identification of hospital outbreaks; and
- the recognition of quality control problems in laboratory testing.
In addition, review of antimicrobial results permits the characterization of:
- resistance mechanisms; and
- the epidemiology of resistant strains.
The WHONET software has the following three principal components.
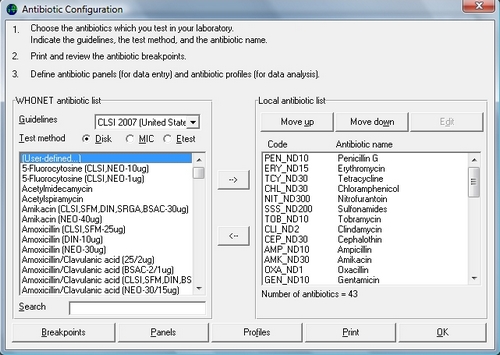
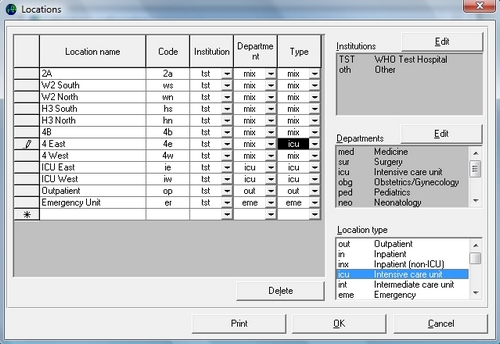
- Laboratory configuration
The system must be configured for your laboratory by specifying information such as the antibiotics tested and the patient care areas served. In addition, you can also indicate what data fields you want included in the data files. This configuration can be modified subsequently. - Data entry
WHONET allows the routine entry of susceptibility test results as well as the retrieval, correction and printing of clinical records. An option is the provision of immediate feedback to technicians on strain phenotypes. If data are converted from an existing laboratory system, direct entry of data into WHONET is unnecessary. - Data analysis
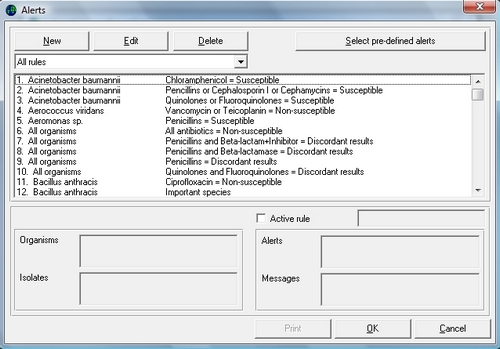
Currently supported analyses include isolate line-listings and summaries, tabulation of resistance statistics, zone diameter and MIC histograms, antibiotic scatterplots and regression curves, and antibiotic resistance profile line-listings and summaries.
More information can be found here http://www.who.int/drugresistance/whonetsoftware/en/
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|







 In this section you'll find a list of companies and organizations working in the healthcare IT sector in Egypt.
In this section you'll find a list of companies and organizations working in the healthcare IT sector in Egypt.